Non Invasive Cardiac Diagnostics
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
What is an Electrocardiogram?
Electrocardiogram or ECG is the oldest heart test that is still in routine use today.
The ECG is a method of recording the electrical activity of the heart. Each heartbeat is caused by a section of the heart generating an electrical signal, which then conducts through specialized pathways to all parts of the heart. These electrical signals also get transmitted through the chest to the skin where they can be recorded.
How is the test performed?
An ECG is performed by placing 12 recording leads at certain specific locations on the body. They only record the heart’s electrical activity. They do not produce any electricity of their own. The recording itself takes only a few seconds. Including the setup time and the time to disconnect the leads, the whole procedure takes about 5 minutes.
It is preferable to perform ECG in a relaxing and resting condition. It is usually done by an ECG technician. There is no need for the presence of a physician.
How to prepare for taking the ECG?
It does not require any preparation except for possibly shaving chest hair to get a better recording.
Before the ECG tell your doctor if you are taking any medications.
There are no restrictions for food or fluids. However, ingestion of cold water immediately before an ECG may produce changes in one of the waveforms recorded (the T wave). Exercise (such as climbing stairs) immediately before an ECG may significantly increase your heart rate.
You may be asked to remove all jewelry and to wear a hospital gown.
How will the test feel?
An ECG is painless. The test has no known side effects. When first applied the electrodes may be cold and in rare circumstances, you may develop a localized rash or irritation where the patches are placed.
Why are 12 leads used in an ECG?
Looking at the heart with 12 leads is like looking at a building from multiple angles. The more points of view you have, the more you learn about it.
By looking at the electrical patterns on an ECG your doctor can determine :
- The nature of an erratic heart beat. There are many different types of abnormal heartbeats. Not all require treatment. In those that do, the ECG recording lets the doctor know which treatment is best.
- The presence of a heart attack. It can also be determined whether the heart attack is old or recent.
- The possibility that there are narrowed arteries in the heart which may lead to a heart attack in the future.
- Whether or not the heart is the reason for the discomfort in the chest.
- The possibility of congenital heart disease.
What are components in an ECG?
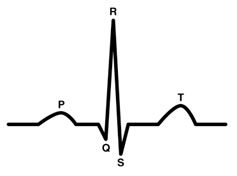
A typical heart beat has three components in a ECG.
The P wave represents the electrical impulse traveling across the atria of the heart (the filling chambers on the top)
The next spike is called the QRS complex, which represents the electrical impulse as it travels across the ventricles, the major pumping chambers of the heart. Abnormalities in QRS are often seen when there has been damage to the ventricular muscle like in heart attack.
The T wave represents the recovery period of the ventricular muscle after it has been stimulated. Abnormalities in ST segment and T wave are seen when heart muscle is ‘ischemic’ that is when it is not getting enough oxygen because of blockages, clot or spasm.
How useful is the resting ECG in detecting CAD in a person without symptoms?
Since ECG measures the electrical conductivity of the heart muscle, the conductivity will not be altered till the muscle is damaged as in heart attack. Even when a coronary artery is almost completely closed, as long as the blood can get through to nourish the muscle that muscle will be unharmed and will usually appear normal in an ECG taken at rest
Moreover ECG does not reflect the performance of the heart. A person may have a clearly abnormal ECG but may be able to run a race, whereas another person may have a normal ECG and may die within a few hours. Studies have shown that in 50% of the coronary patients resting ECG does not show any significant abnormality.
As a result of these, the ECG is no more effective than a stethoscope in the early detection of Coronary Artery disease.
Tread Mill Test (TMT)
What is Tread Mill Test or TMT?
It is also called Stress ECG.
It is quite common for people to have heart disease and still have a normal ECG which was performed under resting conditions. The ECG can become abnormal when the heart is made to work harder. This is the basis for stress test.
The most common way to stress a person’s heart is to have them perform exercise. Walking on a treadmill is most commonly used. For patients who are unable to exercise, intravenous medicines can be given in place of exercise to make the heart work as hard as if the person was running.
Stress tests are commonly used tests for initial screening for CAD. These tests are able to detect the presence of flow-limiting blockages in the coronary arteries generally in the range of at least a 50% reduction in the diameter of at least one of the three major coronary arteries.
What are the types of Stress Tests?
There are two basic types of stress tests
- Those that involve exercising the patient to stress the heart (exercise cardiac stress tests) and
- Those that involve pharmacologically stimulating the heart to mimic the stress of exercise (physiologic stress testing). especially for patients who are unable to exercise.
Why is Stress ECG done?
Stress ECG is done for the following reasons
- To see if an asymptomatic person has already suffered a silent is chemia.
- To determine if a person’s symptoms such as chest discomfort or difficulty in breathing are due to heart disease or some other problem.
- To check whether the treatment given for a patient for blocked arteries is working properly.
- To assess a person’s exercise tolerance before beginning an exercise or cardiac rehabilitation program
How is the test performed?
All stress tests are performed with continuous monitoring of the electrocardiogram (ECG). As the heart works harder certain characteristic abnormalities can develop in the ECG in patients who have underlying heart disease.
The exercise or medication infusion is performed under the supervision of a physician.
The exercise or medication infusion is stopped immediately if:
- An abnormality of the heart is detected.
- The desired peak level of stress is reached. (Also called Target Heart Rate)
- The patient is unable to continue due to the development of any type of symptom.
- The patient asks to have the test stopped due to fatigue or some other reason.
What are the preparations required for TMT?
The only preparation for a stress test is that you must not eat or drink for the six hours preceding the test. If it is an exercise test, make sure you wear loose fitting comfortable clothes and good running shoes. High heels don’t work on a treadmill! Your physician may want you to skip some of your usual medications on the day of the test. Be sure to check with your physician about this.
How accurate is the TMT in diagnosing CAD?
Stress tests are not perfect. Sometimes they come out abnormal when the heart is really okay and sometimes they are normal when there really is a problem with the heart.
The accuracy of the TMT in predicting significant heart disease is variable depending on the risk of having heart disease. In a patient at high risk for heart disease, eg. advanced age, multiple coronary risk factors, an abnormal TMT is very predictive of the presence of heart disease. However a relatively normal TMT may not reflect the absence of significant disease in a patient with the same risk factors (false negative)
Conversely in a low- risk patient a normal TMT is very predictive of the absence of significant heart disease but an abnormal test may not reflect the true presence of heart disease (so-called “false-positive test).
The TMT can miss the presence of significant heart disease in many cases. Unfortunately only about 65% of patients are diagnosed correctly with this test and the accuracy is even less for women.
A false-positive test can occur due to a variety of physiological and cardiac circumstances. About 10% of healthy patients, particularly younger people will have abnormal test results (false positive)
What if I can’t perform an exercise test or I am unable to exercise adequately for a TMT?
Sometimes you can’t do an exercise test because you’re too sick or have physical problems. In this case some drugs are given. This drug increases blood flow to the heart and thus “mimics” an exercise test.
Many patients are unable to exercise maximally for stress testing due to a variety of conditions including arthritis, severe lung disease, severe cardiac disease, orthopedic conditions and diseases of the nervous system. In such patients other tests such CT Angiography or Dobutamine stress test is done.
What if the TMT shows positive?
The doctor may want further tests to evaluate whether it is true positive and to find out the extent of disease.
Echocardiogram
What is an Echocardiogram? Why is the test performed?
An echocardiogram is also known as ultrasound examination or sound wave picture of the heart. It uses the same technology that is used to take pictures of the fetus in pregnant women.
This test is performed to evaluate the valves and chambers of the heart in a non-invasive manner. It allows doctors to evaluate heart murmurs, check the pumping function of the heart and evaluate patients who have had heart attacks. It is a very good screening test for heart disease in certain groups of patients
What is the procedure?
A doctor or a highly trained technician places a hand-held ultrasound probe against the patient’s chest. The probe is connected to a large computer with a video screen. The probe emits sound waves that pass through the chest to the heart. The heart then reflects those sound waves back to the probe. The probe transmits those reflected signals to the computer which reconstructs them into a picture of the heart. This picture is displayed on the screen and then doctor makes a report of his finding.
Is the Echocardiogram test safe?
Yes, it is. There are no known harmful side effects from these sound waves. The test does not hurt because no needles are routinely used and nothing is placed inside the patient. The average test takes about 10-30 minutes.
No patient preparation is required for an echocardiogram. The test can be done anywhere at any time. You’re even allowed to eat before this test!
What does an echocardiogram show?
- The sizes of the 4 chambers of the heart.
- The pumping capacity of the heart (Ejection fraction) Normally it should be in the range of 60-70%.
This is very useful to doctors in assessing the damagedone by heart attacks and to determine how best to treat a patient with heart failure. - Movement of the various parts of the heart muscle especially after heart attack. This can be regional (RWMA) or global.
- Walls of the heart – Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH), Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
- The presence of fluid around the heart. This condition is known as pericardial effusion. An echocardiogram is the quickest way to diagnose this condition.
- Problems with the valves of the heart. The decision whether a person with valve disease require an heart surgery is often made by an echocardiogram.
Can 2D ECHO tell you whether blockages are present or not?
Unfortunately they do not. They do not give the picture of the arteries of the heart. Other types of tests are required to diagnose this condition. However an echo cardiogram can give indirect evidence that a person has blocked arteries by examining the strength of the heart muscle. Ultrasonic contrast agents can also show the amount of blood the heart muscle is receiving.
What is a Trans- Esophageal Echocardiogram?
Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) uses the same sound wave technology that a regular echocardiogram uses but the pictures are taken by inserting a special probe into the esophagus (the food tube that connects the mouth with the stomach) rather than by placing it on the patient’s chest wall. An overnight fasting is required for this test.
This test is done for several reasons:
- In some people, a regular echocardiogram cannot get good pictures of the heart due to the anatomy of their chest. Taking the picture from the esophagus circumvents that problem.
- In some people, the part of the cardiovascular system the physician is interested in taking pictures of is not accessible by a regular echocardiogram.
- Sometimes the regular echocardiogram shows something that is only suggestive of abnormality. To find out for sure a transesophageal echocardiogram is required.
CT Angiography
What is Coronary Calcium Score Scan?
In this test pictures are taken of the heart to look for the presence of calcium deposits in coronary arteries. Calcium deposits are a very specific sign of coronary artery disease. Hence this test is done to rule out Coronary Heart Disease. A high Calcium score indicates higher chance of plaque deposition. Unlike CT coronary Angiogram, X ray contrast is not injected into the blood.
| Normal | – | 0 |
| Mild | – | < 150 |
| Moderate | – | 150 – 400 |
| Silver | – | > 400 |
What is CT Coronary Angiogram?
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CTA) is a non-invasive heart imaging test to determine if either fatty or calcium deposits (plaques) have built up in the coronary arteries. It is used for
- Diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Diagnosis of in-stent restenosis
- Evaluation of coronary bypass graft patency
Do I need to be on fasting for CTA?
It is not necessary to go without food or drink before the procedure but a full stomach is not advisable as this together with the contrast agent might make you feel nauseated. However each radiology facility will ask you to follow their own requirements regarding any fasting before the test.
How is CT Angiogram done?
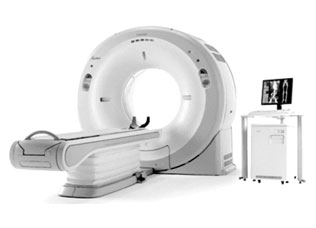
A CT scan technician will guide you into the CT scanning room, where you’ll see a table and a large, doughnut-shaped device called a gantry. You will be made to lie down on the padded table and asked to lie very still during the scan and hold your breath for a brief time to minimize any body movement.
You will receive an injection of IV fluid contrast to outline the coronary arteries and structures so the physicians can better view your heart and coronary system. During the scan you may hear a humming noise but you will not feel anything unusual. You may feel the table move while images are being taken at certain locations of your body. The technician will be monitoring you during the entire exam through a window and can communicate with you via an intercom.
A medication to slow the patient’s heart rate (Beta Blocker) may be given in some cases where heart rate is high.
During a cardiac CT scan an x-ray machine will move around your body in a circle. The machine will take a picture of each part of your heart. It will take about 1- 2 hours though the actual scan occurs in just few minutes. The computer will put the pictures together to make a three-dimensional (3D) picture of the whole heart.
What does 64-slice mean?
The number refers to the number of slices the CT scanner can image in a fraction of a second. A 64 slice scanner produces 64 images per rotation. This takes approximately 5 seconds. CT scanner offers the ability to provide a compressive view of the coronary arteries in 5 heart beats.
Are 256 and 320 slice CT scanners better?
It seems just like yesterday when we were thinking that 64 slice CT scanners are the best and the latest thing in cardiac diagnostics. But technology is moving forward and now there 256 slice and 320 slice CT scanners.
The newer scanners promise greater diagnostic accuracy of CT coronary angiography. But the current thinking is that compared to the cost and accuracy of 256 or higher to a 64 slice scanner, most cardiac associations are of the opinion that 64 slice is good enough.
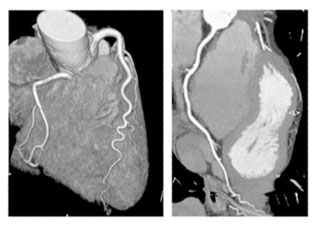
Does CTA have a high radiation exposure?
A The reported effective radiation doses for retrospectively gated, single-source, 64-slice CT scanning have ranged from 9.5-21.4 mSv as compared to 0.02 mSv of a single chest X ray. However, various technologies and techniques have made it possible to lower the dose to less than 5 mSv, and doses of less than 1 mSv are possible in some patients.

